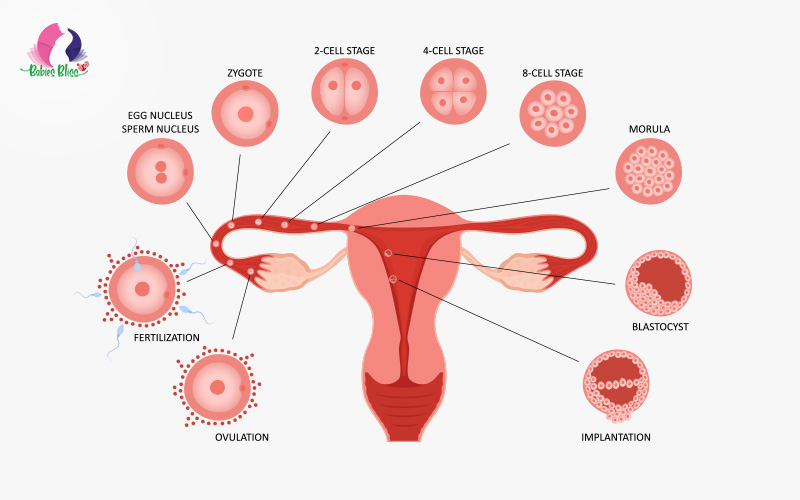
During ovulation, a mature egg is released from one of the ovaries, significantly increasing the chances of pregnancy. But did you know that some women may experience the absence of ovulation? This condition is known as anovulation and can impact fertility and reproductive health, potentially leading to complications. The diagnosis of female infertility associated with anovulation typically involves a medical history review, physical examination and various tests. In this article, we cover everything you need to know about anovulation, from the causes, symptoms and treatment, to providing deeper insight into this topic.
What Causes Anovulation?
In general, anovulation stems from an imbalance in one or more hormones crucial for ovulation. Disruptions in the delicate interplay of these hormones can interfere with the development and release of a mature egg from the ovary. Below are some key examples of hormonal imbalances that may result in anovulation.
High levels of androgens
Androgens are a group of hormones primarily responsible for male traits and reproductive activity, although they are also present in females in smaller amounts. High androgen levels can interfere with the normal development and release of eggs from the ovaries, leading to irregular or absent ovulation.
Pituitary gland dysfunction
Pituitary gland dysfunction refers to abnormalities in the function of the pituitary gland, a small gland located at the base of the brain that produces and regulates various hormones essential for the body’s growth, metabolism, and reproductive function. This can disrupt the secretion of certain hormones, which are crucial for stimulating ovarian follicle development and triggering ovulation.
High levels of prolactin
Prolactin is a hormone primarily responsible for lactation and milk production in breastfeeding women. Elevated levels of prolactin, also known as hyperprolactinemia, can affect normal menstrual cycles and ovulation.
Low levels of thyroid hormones
Thyroid hormones are essential for regulating metabolism, growth and development throughout the body. A decreased production can impair the release of reproductive hormones necessary for ovulation and fertility support.
Low levels of gonadotropin-releasing hormone
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) is a hormone produced by the hypothalamus, a region of the brain. It regulates the release of two important reproductive hormones from the pituitary gland that stimulate ovulation. Dysfunction or irregular secretion of GnRH can disrupt the normal menstrual cycle and contribute to anovulation.
Learn more: Top 5 Tips To Balance Your Hormones Naturally Before Pregnancy
What Are the Symptoms of Anovulation?
Anovulation symptoms are usually associated with the menstrual cycle because this condition influences the hormonal processes that control menstruation. Common symptoms include late or irregular periods, spotting mid-cycle or a period that lasts longer than usual. Additionally, since the hormones are affected, acne, hirsutism (excessive hair growth), or weight fluctuations may also manifest in conjunction with menstrual irregularities.
How Is Anovulation Treated?

While anovulation can be stressful and worrisome, there are fortunately several treatment options to help address this condition. Hormonal medications may be prescribed to induce ovulation or regulate menstrual cycles. It is always recommended to consult your healthcare professional before taking any form of medication.
Patients can also manage anovulation with lifestyle changes. Minimising stress through techniques such as meditation, yoga, or mindfulness regulates the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis, which is crucial for ovulation. Maintaining a healthy weight with a balanced diet and regular exercise improves hormonal balance and enhances ovulatory function as well. If you are one to engage in intense or excessive exercise, try reducing the frequency and intensity of workouts to prevent disruptions in menstrual cycles and promote regular ovulation.

For those who are experiencing infertility related to anovulation, in vitro fertilisation (IVF) can help to increase female fertility. During this process, a woman’s ovaries are stimulated with hormonal medications to produce multiple eggs, which are retrieved through a minor surgical procedure. These eggs are then fertilised with sperm and the embryos are left to culture for a few days. Once developed, one or more embryos are transferred into the woman’s uterus, with any remaining typically frozen for future use.
Infertility is a discouraging and frustrating obstacle to overcome, especially for women who are trying to conceive. However, the right treatment plan in combination with guidance from a professional can make all the difference in changing this course for a more successful endeavour.
Still wondering how a woman can boost her fertility? At Babies Bliss, we’re all about fertility wellness. Not only do our services help clients relax, but they support egg quality too for their oocytes and retrieval process.